Focus
A new initiative to estimate trade in services by mode of supply (TisMoS)
The lack of trade in services data by mode of supply hampers analysis, monitoring and formulation of trade policy. Since information provided by national statistical offices is scarce, the WTO Secretariat, funded by the European Union, is developing an experimental dataset.
Methodology
This new dataset is constructed in line with the Manual on Statistics of International Trade in Services 2010 (MSITS 2010) and the methodology has been updated following experts' feedback.
Balance of Payments
The joint WTO-UNCTAD-ITC balance of payments dataset (BOP) is complemented with estimates to fill in data gaps in the selected EBOPS2010 breakdown for measuring modes 1, 2 and 4. Then some refinements are made to align these data to the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) needs:
- Some balance of payments transactions include the purchase of goods and services supplied or received (for instance, travel and construction). An estimation of the goods part is needed to isolate the service component.
- The GATS services classification W/120 covers distribution services as a separate sector, while in BOP these services are included in the valuation of goods.
Simplified approach
As recommended by the MSITS 2010, the allocation of modes follows a simplified approach that allocates services exports to one dominant mode of supply or, where there is no single dominant mode, to the most significant modes of supply according to a distribution table. This requires assumptions on how specific services are most likely to be supplied. Therefore, the dataset on trade in services by mode of supply is considered an analytical and not a statistical dataset.
Individual country experiences
A number of countries have carried out sector-specific or one-time studies to test the feasibility of regular data collection or to source information on the functioning of priority sectors of their economy. The result of these studies is included in the distribution table for the countries that provide such information.
The idea of presenting trade in services by mode of supply is supported by the Task Force on Modes of Supply, launched by Eurostat, which encourages countries to allocate resources for collecting more information on the distribution of trade in services by mode of supply. In the future, the results of new pilot studies will help to improve the estimates at country and global level.
FATS
Commercial presence (GATS mode 3) is approximated using the Foreign Affiliates Statistics (FATS). This framework describes the activities of foreign-controlled affiliates in the reporting economy (inward FATS) and, conversely, the activities of majority-owned affiliates of resident enterprises established abroad (outward FATS). The existing data sources are combined and completed with estimates to build a worldwide FATS dataset.
Bridge table
The FATS framework provides information on domestic sales/output according to an activity breakdown, namely the ICFA, whereas BOP data is classified mainly by product. To this day, no clear-cut correspondence exists between ICFA, Rev. 4 and EBOPS 2010 (BPM6). Therefore, a bridge table is created with additional items to better meet the GATS needs. For example, all EBOPS 2010 items referring to health, to education services, or to business travel (and tourism) are grouped together and linked to the corresponding ISIC sector.
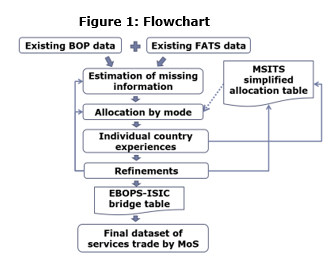
Final dataset
The final dataset contains both import and export services flows broken down by product and by mode for 215 reporting economies from 2005 onwards. The dataset is well documented with every data point identified by a flag to indicate its respective metadata. Its release is scheduled for March 2019.
Results
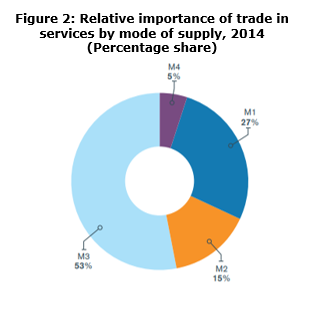
First results as to the relative importance of modes reveal that mode 3 (commercial presence) is the dominant mode. Mode 1 (cross-border supply) is estimated to account for 27 per cent of total services trade. mode 2 (consumption abroad) accounts for 15 per cent and mode 4 (presence of natural persons) accounts for less than 5%. These first results at a global level do not reveal the significant variability across countries and sectors. In addition, this first distribution at a global level may change with the advent of digital trade.
Eurostat activities on international trade in services by modes of supply
International trade in services by Modes of Supply (MoS) shows how services are supplied internationally. According to the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) there are four modes of supply: mode 1: cross-border delivery e.g. by electronic means; mode 2: client travels abroad to the country of the supplier; mode 3: affiliate is established abroad and mode 4: the supplier travels abroad to the country of the client.
Statistics on services by mode are important to policy makers and trade negotiators as they allow for a better understanding of how and where services are supplied internationally. Eurostat has estimated the services exported and imported by modes using a pilot model, based on the MSITS 2010 simplified methodology. Several EU member states have also applied the methodology, with or without adjusting the model according to the country's specificities. According to the model, in 2015 about two thirds of services supplied from the 28 EU member states to non-EU countries were provided through affiliates established abroad (mode 3), less than one third by cross border transactions (mode 1), and about 10% by consumption abroad (mode 2) and presence of natural persons abroad (mode 4).
These estimates are based on the annual international trade in services statistics (Balance of Payments framework), foreign affiliates statistics (FATS) and trade in goods statistics. Eurostat has published an online article on MOS.
Eurostat has launched a task force on further developing the MoS methodology. Thirteen EU member states participate in the task force together with the European Commission's Directorate-General for Trade, the United States Bureau of Economic Analysis, the ECB, OECD, WTO, and the UNSD. The task force has already had two meetings (2017 November and 2018 April) and will have its next meeting in March 2019.
E-learning courses on merchandise trade statistics and trade in services statistics - UNCTAD
Building on the success of their E-learning course on international trade in services statistics, finalized in 2016, UNCTAD, WTO and UNSD are in the closing stages of the elaboration of a similar on-line training for merchandise trade data, based on the IMTS-2010 concepts. The merchandise trade e-learning track, being developed in English, would be tested and validated in 2018 with a selected group of countries.
The two courses are administered by the UNCTAD's Train-for-Trade Team and they primarily target the compilers and producers of statistics. Both courses cover six training modules and are essentially structured as follows:
- statistical concepts and the importance of quality data
- institutional arrangements and other prerequisites for data collection
- data sources, collection and compilation
- metadata and quality
- dissemination and analysis, and
- new areas of work
Since it became operational in spring 2016, 398 participants from some 90 countries took the trade in services statistics e-learning training. WTO used the course as a prerequisite for the participation in two more advanced seminars they organized for LDCs', African and other developing economies' statisticians. The services E-learning modules, initially in English, will soon be available also in French.
The UNCTAD E-learning is usually organized for a group of countries based on a joint official request sent through government agencies, regional or international organizations.For information: statistics@unctad.org
Methodology
NCDP Report
The NATIONAL COMPILATION AND DISSEMINATION PRACTICES provides an overview of national compilation and dissemination practices and their compliance with the recommendations contained in International Merchandise Trade Statistics: Concepts and Definitions 2010 (IMTS 2010) and compilation guidelines outlined in International Merchandise Trade Statistics: Compilers Manual, Revision 1 (IMTS 2010-CM). The overview reflects responses to the 2017 National Compilation and Dissemination Practices (NCDP) survey, which was drafted by UNSD, reviewed by other TFITS members, and sent out jointly by UNSD, OECD and WTO to national trade statistics compilers in 2017.
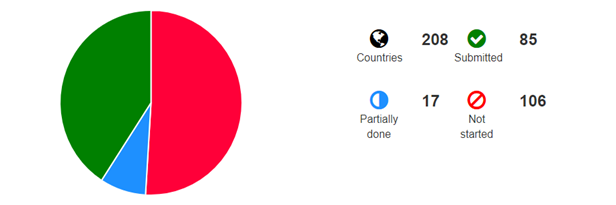
The responses of the survey are available at UN Comtrade website of https://comtrade.un.org/survey/reports. It shows overall status of submission such as “Not Started”, “Partially Done” and “Submitted”. It is expected that the survey website to be kept available to allow countries’ submission in due time.
To facilitate data query, the reporting site is categorized by country https://comtrade.un.org/survey/Reports/byCountry
and by question https://comtrade.un.org/survey/Reports/byQuestion.
BEC Correlations
The working papers on BEC / HS /EBOPS correspondence tables are available at UNSD website: https://unstats.un.org/unsd/trade/classifications/bec.asp. The principles of establishing these transpositions are as follows: https://www.wto.org/english/res_e/statis_e/wts2018_e/wts18_toc_e.htm
- 1st LEVEL (BEC dimension): Map HS sub-headings and CPC classes to the first top level of broad economic categories
- 2nd LEVEL (Product dimension): Map goods and services accordingly
- 3rd LEVEL (End-use dimension): Even though, this may be challenging, but for goods, we can reuse (and review) existing correlations between BEC 4 and HS 2012
- 4th LEVEL (Processing dimension): Similar with 3rd level, for goods, we can refer to existing correlations between BEC 4 and HS 2012
- 5th LEVEL (Specification dimension): This is new dimension, therefore requires more research to establish correlations. The idea is to identify position (downstream/upstream) of goods/services within value-added chain
- 6th LEVEL (Durability dimension): Similar with 3rd and 4th levels, we can reuse existing correlations between BEC 4 and HS 2012 for goods
Technical Cooperation and Seminars
Regional Training Workshop on Trade SDMX
Tunis, Tunisia, 10-14 September 2018
Statistical Data and Metadata Exchange (SDMX) is a preferred data transmission standard on statistical data as noted in UN Statistical Commission report on Decision 12 on its thirty-ninth session (2008). And in addition, SDMX is an ISO standard (ISO 17369:2013) designed to describe statistical data and metadata, normalize data exchange and improve their efficient sharing across statistical and similar organizations.
An inter-agency working group consisting of Eurostat, the International Trade Centre (ITC), the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD), and the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) have been working to specify uniform structures, concept definitions and code lists for the transmission of IMTS data and metadata in accordance with SDMX, called SDMX-IMTS or simply Trade SDMX.
Within this context, African Union Commission (AUC) and UN Statistics Division (UNSD) organize jointly the first Regional Training Workshop on Trade SDMX to raise awareness on SDMX-IMTS artifacts including data structure, concepts and code lists; and to train IT experts and trade statisticians in using latest SDMX tools to map their trade database in to SDMX-IMTS output. The workshop will take place in Tunis, Tunisia from 10 to 14 September 2018 and will be attended by around twenty-five African countries and various Regional Economic Communities.
For more information, visit the Regional Training Workshop on Trade SDMX.
Regional validation workshop on International Merchandise Trade Statistics
Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago, 15-18 May 2018
The Regional validation workshop on International Merchandise Trade Statistics (IMTS) is organized as a follow-up activity to the distance-learning course on International Merchandise Trade Statistics, delivered for the first time (to more than 130 participants from 28 countries) to contribute to enhance the knowledge and the capacity IMTS professionals, mainly from the English-speaking countries from the Caribbean region and Asia.
The main goals are to enhance statisticians' ability to apply the most recent internationally agreed recommendations on IMTS, define best possible data sources, set up adequate (or enforce existing) collection systems, and enhance statistics compilation processes. Moreover, the course would communicate the importance of quality, metadata, timely dissemination, and links to economic analysis and national policy objectives.
For more information, visit the Regional validation workshop on International Merchandise Trade Statistics.
Meeting of the Expert Group on international trade and economic globalization statistics
Rome, Italy, 7-9 May, 2018
Economic globalization has created new opportunities for businesses to organize their production chains more efficiently. This has increased the complexity of compiling economic statistics, as it is more difficult to break down production activities on a country-by-country basis. There is a need to understand the cross country benefits and risks by being able to “look through” the global firms in the global value chains (GVCs) and see their contributions in the production networks of resident enterprises in multiple countries. These emerging global production arrangements pose challenges to macroeconomic and business statistics, including the supporting business registers. The challenges include the choice of the statistical unit, the classification of the (global value chain satellite) accounts, the implementation of the principle of economic control and ownership, and the recording of domestic and cross-border transactions and positions in national accounts and balance of payments statistics.
In its decision 46/107, the Statistical Commission established the Expert Group on International Trade and Economic Globalization Statistics to address these measurement challenges. The main task of the Expert Group is to develop a handbook that will account for the measurement of GVCs, as described in various reports to the Commission on this topic in the past five years. Both the GVC perspective and the perspective of the national data compiler are fundamental to understanding the composition of the handbook. However, with the realization of the cross-country impact of GVCs on the economic structure of partner countries, a multi-country perspective for those national industries that are included in major GVCs is encouraged in the handbook.
For more information, visit the Meeting of the Expert Group on international trade and economic globalization statistics.
Publications and databases
UNSD

The International Trade Statistics Yearbook: Volume I – Trade by Country and Volume II - Trade by Product
Trade by Product provide an overview of the latest trends of trade in goods and services showing country and product profiles of international trade, respectively.
And in addition, it contains several trade analytical tables on total imports and exports, external trade conversion factors, external trade indices, indicators of manufactured goods exports and fuel imports, and exports by provenance and destination.
Eurostats

Compilers Guide for statistics on Services Trade by Enterprise Characteristics (STEC)
In November 2017, Eurostat jointly with OECD published the new manual, providing recommendations on how Services Trade by Enterprise Characteristics (STEC) statistics can be compiled. The Compilers Guide for STEC is the outcome of the collaborative work of the STEC task force participants, and is a joint Eurostat-OECD Publication. It builds on the work and expertise of the Eurostat STEC Task Force, provides recommendations on how STEC statistics can be compiled. More specifically, this guide provides methodological guidance on how to produce statistics by linking different statistical datasets as STEC data are typically produced by linking International Trade in Services enterprise surveys with the Statistical Business Register. As a result additional statistical information can be derived from the existing national statistical data sources without increasing the burden to the respondents. This Eurostat-OECD Compilers Guide for Statistics on Services Trade by Enterprise Characteristics is an important tool that facilitates the production of cross-country comparable STEC statistics.
STEC statistics provide insights into how different types of enterprises – characterised for example by their main activity, size, or ownership – are engaged in international services trade. In addition to thereby providing a “profile” of services traders, STEC statistics also contribute to the larger statistical agenda on measuring economic globalization.

Globalisation patterns in EU trade and investment
Globalisation patterns in EU trade and investment highlights some aspects of economic globalisation in focusing on developments related to international trade and investment for the European Union (EU) and its 28 Member States from a business perspective, analysing exchanges between traders and patterns of behaviour within and between enterprises. It presents a broad range of statistics on the balance of payments, international trade and business in a globalised world. The first part is devoted to the role played by the European Union in global trade and investment as compared to its main trade partners. In part two, the publication focuses on the international trade in goods and services, foreign direct investment, and the structure and conduct of foreign affiliates within the EU.
OECD

OECD Statistics on International Trade in Services, Volume 2017 Issue 1
Detailed Tables by Service Category
This OECD publication includes statistics by detailed type of service on international trade in services for the 35 OECD countries, the European Union, the Euro area, Colombia and the Russian Federation.
ISBN: 9789264288447(PDF); 9789264288430 (print)

OECD Statistics on International Trade in Services, Volume 2017 Issue 2
Detailed Tables by Partner Country
This OECD publication provides statistics on international trade in services by partner country for 31 OECD countries plus the European Union, the Euro area and the Russian Federation as well as links to definitions and methodological notes. The data concern trade between residents and non-residents of countries and are reported within the framework of the Manual on Statistics of International Trade in Services. This book includes summary tables of trade patterns listing the main trading partners for each country and by broad service category. Series are shown in US dollars and cover the period 2011-2015.
ISBN: 9789264288546(PDF); 9789264288478(print)
Overview of existing databases covering SITS
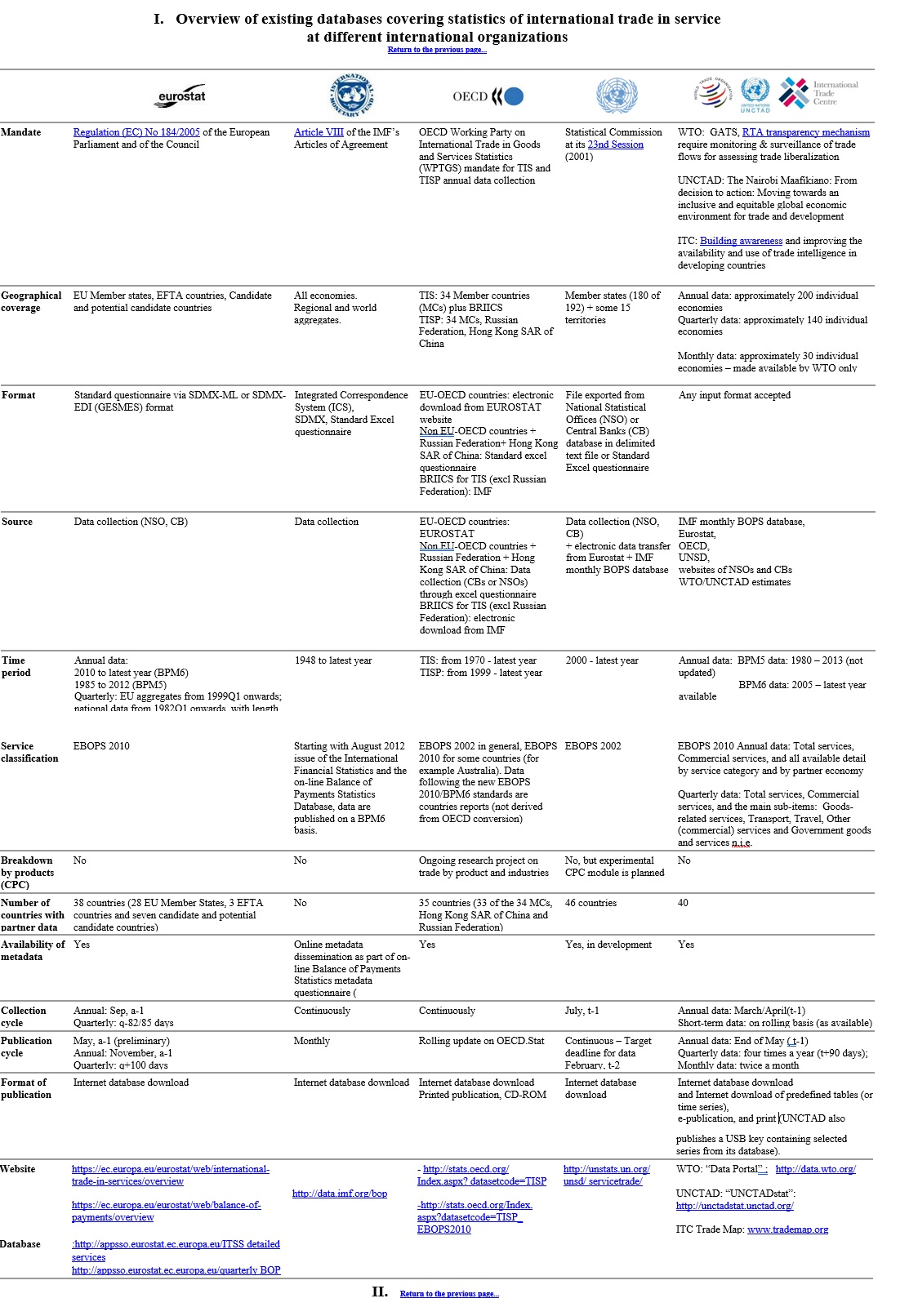

UNCTAD Handbook of Statistics 2018
The new UNCTAD Handbook of Statistics is being released on 5th December 2018. A detailed analysis of recent trends estimated by the nowcast models shows that merchandise trade and trade in services grew robustly during the first half of 2018, although there were significant indications of a slowdown in the second half of the year. A global economic cooldown and adjusted expectations due to recent protectionist trade measures can explain this reverse trend.
The refurbished Handbook includes many maps, charts, and infographics, offering the possibility to seize essential messages at a glance. The accompanying texts analyze recent trends, presenting them by geographical regions, products, individual economies etc. The Handbook further includes principal economic or statistical concepts and definitions, as well as a selection of succinct statistical tables shown at the end of each of the five thematic chapters. Furthermore, the Annex presents the key economic indicators for all individual economies and various country-groups. All figures are sourced from the data sets available online at UNCTADstat. (http://unctadstat.unctad.org)

Key Statistics and Trends in International Trade 2018
This publication gives a status update on trends in international trade over the last few years. The first part gives an overview of the most recent trends and statistics. The second part provides illustrative statistics on international trade in goods and services covering the last 10 years. The second part is divided into two sections. Section 1 provides trade statistics at various levels of aggregation illustrating the evolution of trade across economic sectors and geographic regions. Section 2 presents some of the most commonly used trade indicators at the country level, so as to illustrate trade performance across countries.

Key Statistics and Trends in Trade Policy 2018
This publication informs readers on trade policy measures affecting international trade. The publication is structured in two parts. The first part discusses trade imbalances and their implications for trade policy. The second part illustrates the main trends in selected trade policy instruments by providing key descriptive statistics. The publication covers tariffs, trade agreements, non-tariff measures, trade defense measures, and exchange rates. Trends and statistics are provided at various levels of aggregation illustrating the use of the trade policy measures across economic sectors and geographic regions.
Summary of past, current and planned technical assistance activities and awareness raising relating to services trade statistics, merchandise trade statistics, Tourism statistics and Trade in Value Added statistics
WTO Data Portal
The WTO Data portal, launched in November 2018, brings together a wide range of statistical indicators on international trade and other WTO-related information. Through this data retrieval tool, users may select and download data on international trade – http://data.wto.org/
World Trade Statistical Review 2018
TThe “World Trade Statistical Review” looks into the latest trends in global trade, with in-depth analysis of what is being traded and who the key players are. It also reviews the latest developments in trade policymaking in areas such as trade facilitation and trade-restrictive measures. Analytical chapters are complemented by over 60 tables providing a detailed breakdown of the goods and services being traded and the leading exporters/importers." https://www.wto.org/english/res_e/statis_e/wts2018_e/wts18_toc_e.htm
UN COMTRADE UPGRADE
UNSD has introduced an upgrade of the data production system for international trade statistics in January 2018. This system covers the full production cycle of collection, processing and dissemination for both trade in goods and services. Even though upgrade to production system was completed; the upgrade to dissemination system is on-going (see the update schedule at https://comtrade.un.org/data/doc/UpgradePlan)
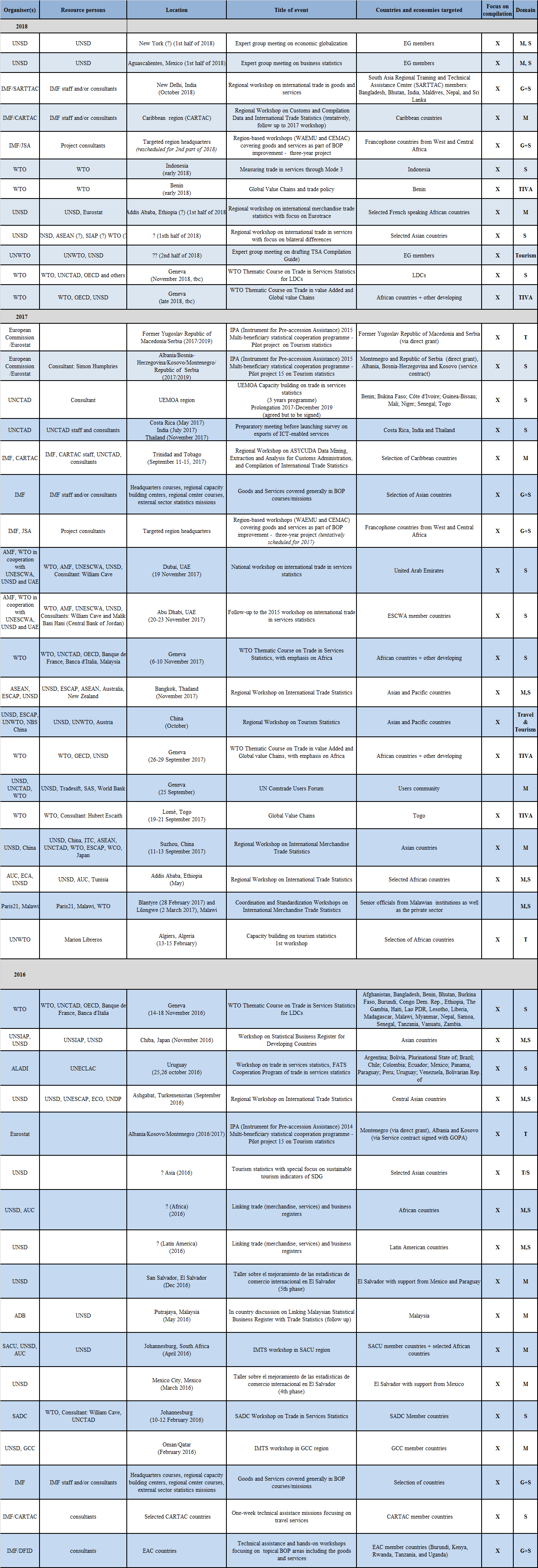
Past Events
Inter-Agency Task Force on International Trade Statistics (TFITS) 9-10 October 2018, Geneva, Switzerland
The most recent meeting of the Inter-Agency Task Force on International Trade Statistics (TFITS) took place in Geneva on 9-10 October 2018. In addition to agenda items for information exchange on methodological and data quality issues related to trade statistics, as well as for updates on newly released datasets and publications, the meeting discussed bilateral trade in goods and trade in services asymmetries, the development of trade in services statistics by modes of supply, and statistical capacity building.
